Virtual Reality: Opportunities & Risks
Virtual reality has the potential to completely change our lives as the lines between our physical and virtual worlds become increasingly blurred. With rapid advances in technology, the possibilities are endless.
This blog is an essential read for clinicians who want to keep up to date with trends in the international gaming industry. It explores what virtual reality currently offers, its future direction and the associated risks of addiction.
What is virtual reality?

Virtual reality (VR) is a computer-generated environment that either simulates the physical world or offers a totally different experience. Users are immersed in their surroundings through a computer or video console, or via a virtual reality headset or helmet.
The history of virtual reality1 dates back to the 1930s with the publication of science fiction novel, “Pygmalion’s Spectacles” by Stanley Weinbaum which introduced the concept of holographic virtual reality. However, it wasn’t until the 1990s that virtual reality became widely accessible to the public through the launch of arcade games and machines.
There are three types of virtual reality2 available today, although technology is advancing rapidly:
- Non-immersive virtual reality – Users engage with a computer-generated environment without being fully immersed in the virtual world – they stay aware of their physical surroundings at all times.
- Semi-immersive virtual reality – This partially virtual environment provides more immersion via 3D graphics but users still remain connected to the physical world.
- Fully-immersive virtual reality – Users feel like they’re actually inside the 3D experience. It offers fully immersive sight and sound simulation via VR glasses or a head mount display.
Although virtual reality has been widely adopted by the gaming industry, it’s being increasingly employed in other sectors to enhance the user experience, streamline business processes, improve safety and train staff:
- Entertainment – movies, museums, galleries, concerts
- Healthcare – medical training, surgery planning, virtual reality exposure therapy
- Education – laboratory experiments, language training, field trips
- Aviation – flight simulation, aircraft maintenance training, in-flight entertainment
- Architecture – industrial design
- Military – training exercises (medical, combat and vehicle).
Where next for virtual reality?
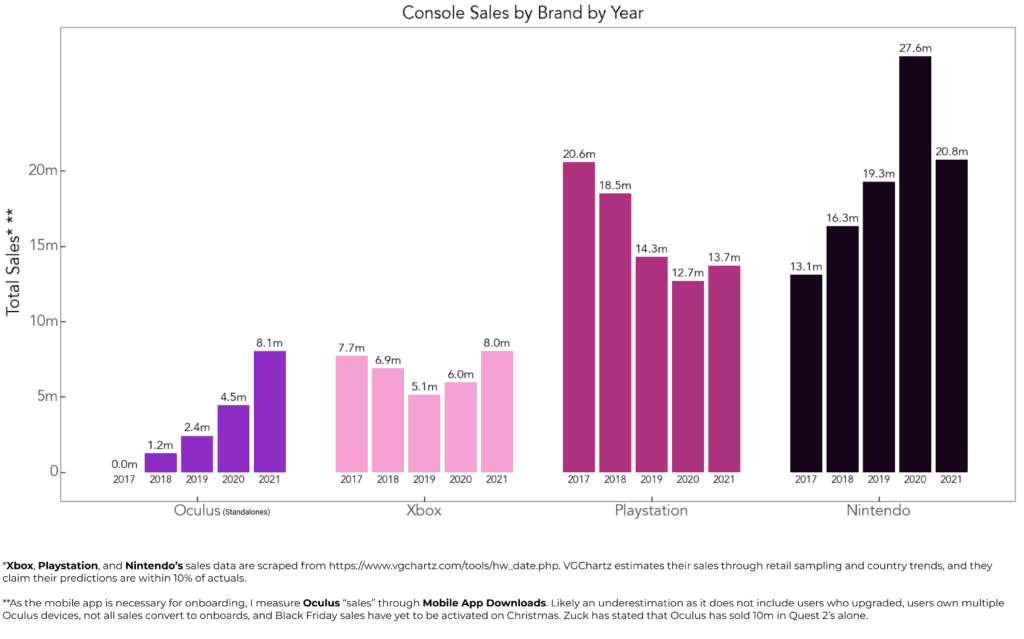
In 2021, Oculus sold more headsets than Microsoft sold Xboxs.
According to Statista3, the global virtual reality market size is forecast to increase from around US$5 billion in 2021 to more than US$12 billion by 2024.
Virtual reality looks set to develop beyond all recognition over the coming years. As the lines between our physical and virtual worlds become increasingly blurred it’s likely that we’ll experience virtual reality in ways that we cannot yet imagine. Forbes4 has made some future predictions of how this technology might reshape our lives:
- Improved smartphone technology will provide a better VR experience on phones
- 5G wireless networks will make virtual reality accessible anywhere in the world
- Hand detection and eye tracking technology will be increasingly incorporated into VR headsets
- New accessories will enhance the immersive experience – robotic boots to simulate walking, full-body haptic suits to replicate feelings of touch and sensation, and augmented reality contact lenses that place information inside the wearer’s eyes.
One future direction of virtual reality is the metaverse – a 3D space that does not yet exist where people can game, work and communicate. Facebook co-founder Mark Zuckerberg5 describes it as “an embodied internet where instead of just viewing content – you are in it.” Meta6 – the new brand that owns Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp and Messenger – is investing US$150 million in virtual reality and augmented reality training and resources to bringing the metaverse to life. Find out more about the metaverse and how it will transform our world.
Virtual reality vs augmented reality
Although virtual reality is being used in many areas of life, there is still some confusion with augmented reality (AR). The main difference is the user experience. Augmented reality overlays digital imagery on a physical-world setting, whereas virtual reality uses a computer-generated environment.
An example of augmented reality in gaming7 is Pokémon Go, a free smartphone game. Players find and capture animated Pokémon characters that pop up in real-world locations – streets, parks, buildings and bodies of water.
Benefits of virtual reality in gaming

As well as enhancing the game experience by making it more immersive, there are other benefits of virtual reality video games:
- Improving physical health – Players don’t spend hours sitting in a sedentary position when VR gaming, they often become more physically active by moving around the room.
- Reducing stress – Immersive video games are a great way to relax and escape from the stress of everyday life.
- Treating mental health issues – Research8 shows that virtual reality can be effective for supporting the treatment of anxiety and depression. It can also be effective when treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as players can confront the situations that cause them fear and anxiety in a safe and controlled environment. The psychological effects of virtual reality are likely to become more powerful as the technology develops.
- Overcoming phobias – VR games can help players overcome their biggest fears – heights, flying, snakes, sharks, water or darkness – in order to win the game.
Find out more about the benefits of gaming.
Risks of virtual reality in gaming
There are also negative aspects of virtual reality gaming:
- Virtual reality sickness – VR gaming can disrupt the sensory system and cause similar symptoms to motion sickness – nausea, dizziness, headaches, fatigue and loss of balance.
- Other health risks – Users of virtual reality have reported a number of other harmful effects9 including broken bones and torn ligaments (after colliding with walls, objects and other players), vision damage and even seizures.
- Virtual reality addiction – As VR technology becomes more immersive, there is an increased risk of virtual reality addiction (also known as virtual gaming addiction). Players can become VR addicts, wanting to spend more and more time in their simulated environment, away from the stress and pressures of everyday life. According to research by the Higher Colleges of Technology10: “The negative impacts of VR gaming addiction are like any media addiction. As with any media addiction, playing VR games for hours can cause serious mental illnesses such as depression, anxiety, attention deficit disorder, and in many cases, autism spectrum traits and features, obesity, sleep problems, increased aggression. The main impact of playing VR for long hours is that it may damage the brain in a way that people will not be able to distinguish between VR and reality.” This behavioral addiction is a subset of internet addiction and gaming disorder. Find out more about the signs of internet addiction, the health consequences of gaming and the prevalence of gaming disorder.
How to help clients with gaming disorder
Clinicians need to keep up to date with developments in the gaming industry – including advances in virtual reality – to enhance client engagement and offer culturally competent treatment practices.
At INTENTA, we envisage a future where virtual and augmented reality support our shared well-being. Our Gaming Disorder Clinical Training equips professionals with practical prevention tools and intervention strategies to help players enjoy a safer and healthier video game experience, and move away from compulsive use towards the intentional use of VR technology.
Improve your quality of care for gaming clients and their families. Find out more about our training today.
Footnote:
- https://www.vrs.org.uk/virtual-reality/history.html
- https://heizenrader.com/the-3-types-of-virtual-reality/#:~:text=There%20are%203%20primary%20categories,%2C%20and%20fully%2Dimmersive%20simulations.)
- https://www.statista.com/topics/2532/virtual-reality-vr/#dossierKeyfigures
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2021/06/04/future-predictions-of-how-virtual-reality-and-augmented-reality-will-reshape-our-lives/?sh=296ae0de68b4
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-57942909
- https://about.facebook.com/meta/
- https://www.nytimes.com/2016/07/12/technology/pokemon-go-brings-augmented-reality-to-a-mass-audience.html
- https://mental.jmir.org/2021/9/e29681/
- https://www.lawtechnologytoday.org/2021/01/what-are-the-harmful-effects-of-virtual-reality/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331352607_Virtual_Reality_for_Medical_Science_in_the_UAE
Subscribe to Trends & Insights
Enter your email to receive monthly trends, insights and resources on gaming and digital disorders.
Subscribe to Trends & Insights
Enter your email to receive monthly trends, insights and resources on gaming, esports and mental health.

